
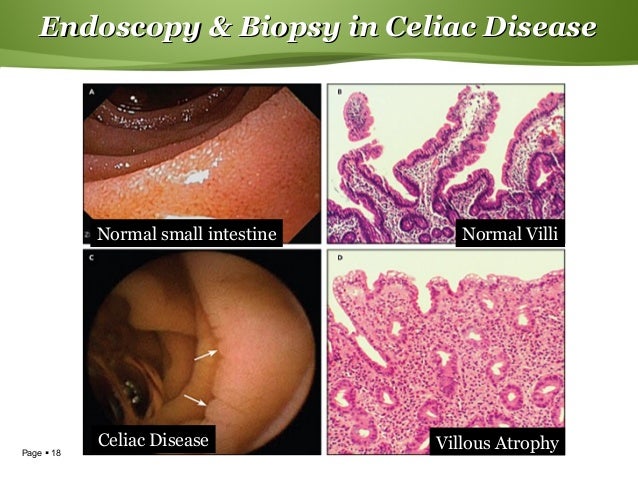

The Spearman correlation coefficient (r = 0.33) revealed a significant association between the methods ( P = 0.002).Ĭonclusions: Changes in the duodenal mucosa detected on EGD were significantly and positively associated with histopathologic findings. Results: Five patients (5.8 %) were EGD I but not Marsh grade 1 25 patients (29.4 %) were EGD II, 4 of whom (16 %) were classified as Marsh grade 2 and 55 patients (64.7 %) were EGD III, 51 (92.7 %) of whom were classified as Marsh grades 3 and 4. EGD types 0, I and II corresponds to Marsh grades 0, 1 and 2, respectively, while EGD type III corresponds to Marsh grade 3 and 4. Out of 109 cases, 85 met the inclusion criteria: conventional EGD combined with chromoendoscopy, zoom and biopsy. Patients and methods: Between January 2000 and March 2010, an electronic database containing 34,540 EDGs of patients aged > 14 years was searched for cases of CD. We investigated the association between endoscopic features and histopathological findings (Marsh) for duodenal mucosa in celiac disease patients and propose an endoscopic classification of severity. Persistent related inflammation of the duodenal mucosa causes atrophy architecture detectable on esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) and histopathology. Triggered and maintained by the ingestion of gluten, celiac disease is a chronic systemic autoimmune disorder affecting genetically predisposed individuals. Background and study aims: Celiac disease (CD) is a chronic systemic autoimmune disorder affecting genetically predisposed individuals, triggered and maintained by the ingestion of gluten.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
